今回はSQL文のDISTINCTについて解説します。
/* Id1 */
data data1;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111; Id4=1111;
output;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111; Id4=2222;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222; Id4=3333;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222; Id4=4444;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333; Id4=5555;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333; Id4=6666;
output;
run;
proc sql;
create table data2 AS
select distinct Id1
from data1 t1;
quit ;
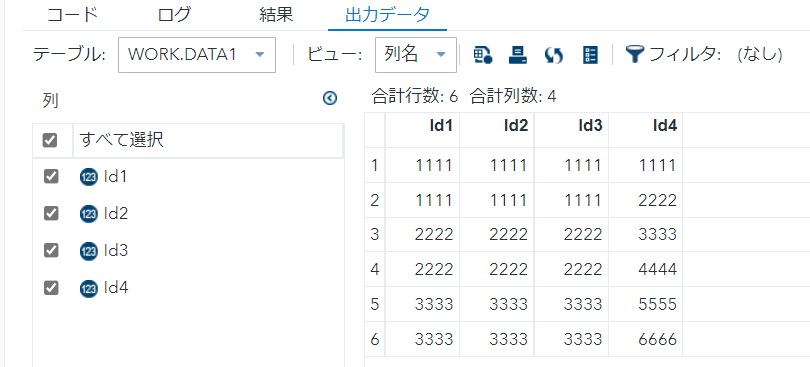
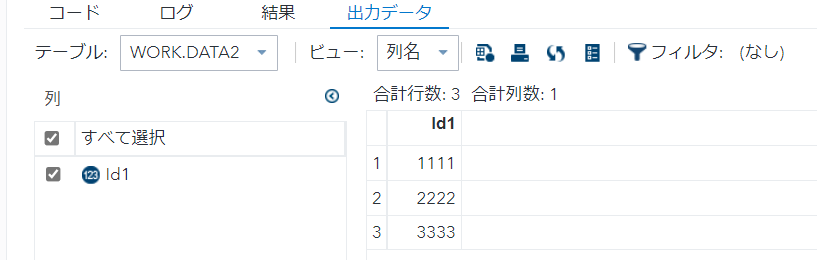
- select句にdistinctを用いると、重複をユニーク化する。
- 今回はId1の重複をユニーク化。
/* Id1,Id4 */
data data1;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111; Id4=1111;
output;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111; Id4=2222;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222; Id4=3333;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222; Id4=4444;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333; Id4=5555;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333; Id4=6666;
output;
run;
proc sql;
create table data2 AS
select distinct Id1,Id4
from data1 t1;
quit ;
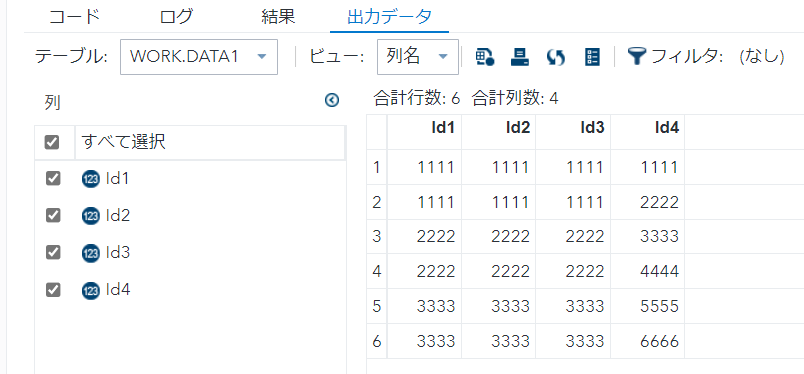
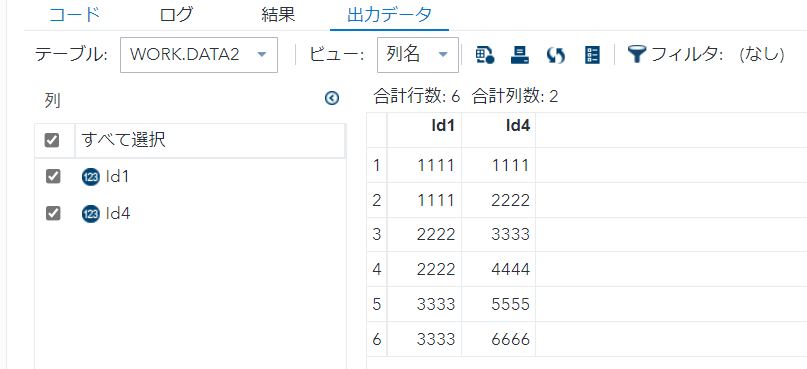
- select句にdistinctを用いると、重複をユニーク化する。
- 今回はId1-Id4の重複をユニーク化。
/* *1 */
data data1;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111;
output;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333;
output;
run;
proc sql;
create table data2 AS
select distinct *
from data1 t1;
quit ;
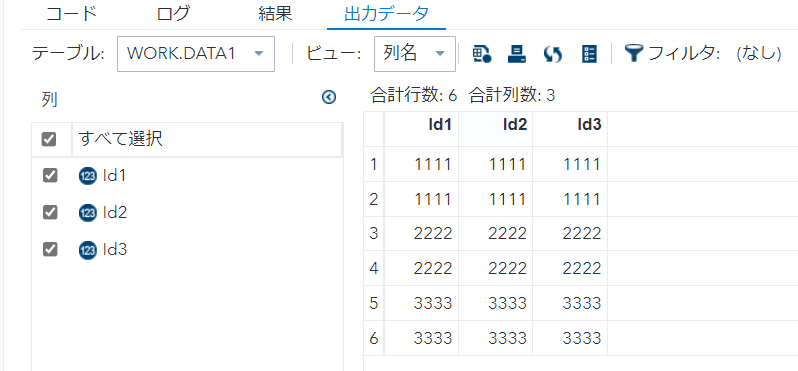

- select句にdistinctを用いると、重複をユニーク化する。
- 今回は全項目での重複をユニーク化。
/* *2 */
data data1;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111; Id4=1111;
output;
Id1=1111; Id2=1111; Id3=1111; Id4=2222;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222; Id4=3333;
output;
Id1=2222; Id2=2222; Id3=2222; Id4=4444;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333; Id4=5555;
output;
Id1=3333; Id2=3333; Id3=3333; Id4=6666;
output;
run;
proc sql;
create table data2 AS
select distinct *
from data1 t1;
quit ;

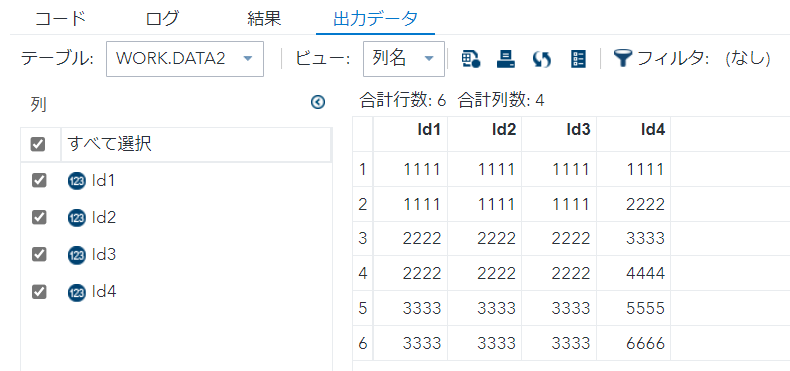
- select句にdistinctを用いると、重複をユニーク化する。
- 今回は全項目での重複をユニーク化。

